The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years Stock market downturns have long been a subject of rigorous academic inquiry, as they encapsulate the complex interplay of macroeconomic variables, investor psychology, and structural market mechanisms. A precipitous decline in stock prices often incites widespread panic, leading to knee-jerk reactions that can compound financial losses. Yet, within such turmoil lies opportunity—savvy investors, equipped with a comprehensive understanding of economic fundamentals, historical market cycles, and disciplined strategic frameworks, can capitalize on undervaluations and fortify their financial positions.

This article presents an advanced analytical framework for comprehending stock market crashes, evaluating their systemic causes, and devising methodical responses. It examines historical market downturns, elucidates behavioral finance principles that exacerbate investor errors, and outlines sophisticated portfolio management strategies designed to mitigate risk and enhance resilience. Ultimately, it furnishes readers with the intellectual tools necessary to navigate extreme market volatility with prudence and strategic foresight.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
Systemic Catalysts of Market Crashes The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
A thorough comprehension of stock market crashes necessitates an examination of their root causes. Several macroeconomic and structural factors contribute to market declines:
- Macroeconomic Contractions – A decelerating economy, characterized by declining GDP growth, diminishing corporate profitability, and rising unemployment, precipitates a loss of investor confidence, leading to sell-offs.
- Monetary Policy Shocks – Central banks, particularly the Federal Reserve, influence liquidity conditions through interest rate adjustments. A contractionary monetary policy—marked by interest rate hikes—dampens borrowing, suppresses corporate expansion, and places downward pressure on equity valuations.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
- Geopolitical and Exogenous Shocks – Wars, trade embargoes, supply chain disruptions, and black swan events (such as pandemics or financial collapses) introduce uncertainty, destabilizing investor sentiment and amplifying volatility.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
- Asset Price Bubbles and Overvaluation – Excessive speculation, fueled by irrational exuberance, often results in asset bubbles. When valuations become decoupled from intrinsic earnings potential, mean reversion triggers abrupt corrections.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
- Market Liquidity Crises – A paucity of liquidity exacerbates market crashes, as investors seeking to exit positions encounter constrained market depth, intensifying downward momentum.
- Behavioral Finance and Herd Mentality – Cognitive biases such as loss aversion, confirmation bias, and recency bias influence investor decision-making, often culminating in herd-driven panic selling.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
Recognizing these catalysts enables investors to exercise informed judgment, mitigating exposure to systemic risks.
Tactical Responses to a Market Collapse
1. Maintain Composure and Avoid Reactive Liquidation
Behavioral finance research underscores that panic selling is a predominant cause of wealth destruction during market downturns. Historical market data reveal that equities, despite periodic declines, have exhibited a secular upward trajectory over extended time horizons. Investors who capitulate during downturns not only lock in losses but also forgo the opportunity for recovery and capital appreciation.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years

2. Conduct a Rigorous Portfolio Diagnostic
A stock market crash warrants a meticulous reassessment of one’s investment portfolio. Critical considerations include:
- Asset Class Diversification – A well-structured portfolio should comprise equities, fixed-income instruments, real estate, and alternative assets to minimize idiosyncratic risk.
- Sector Rotation Analysis – Defensive sectors (e.g., utilities, healthcare, and consumer staples) tend to exhibit lower volatility and superior downside protection during market contractions.
- Risk Exposure Calibration – Evaluating beta coefficients and value-at-risk (VaR) metrics facilitates precise risk quantification and the potential rebalancing of asset allocations.
- Liquidity Assessment – Investors should maintain sufficient liquid reserves to weather prolonged volatility without necessitating premature asset liquidations.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
3. Strategic Cash Reserve Deployment
Liquidity assumes paramount importance during a downturn. Maintaining an emergency fund equivalent to at least six months of expenses ensures financial stability, while strategic cash reserves enable opportunistic acquisitions of undervalued assets. Investors should consider allocating capital incrementally via dollar-cost averaging (DCA) to mitigate the risk of adverse market timing.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
4. Discerning Value in Market Dislocations
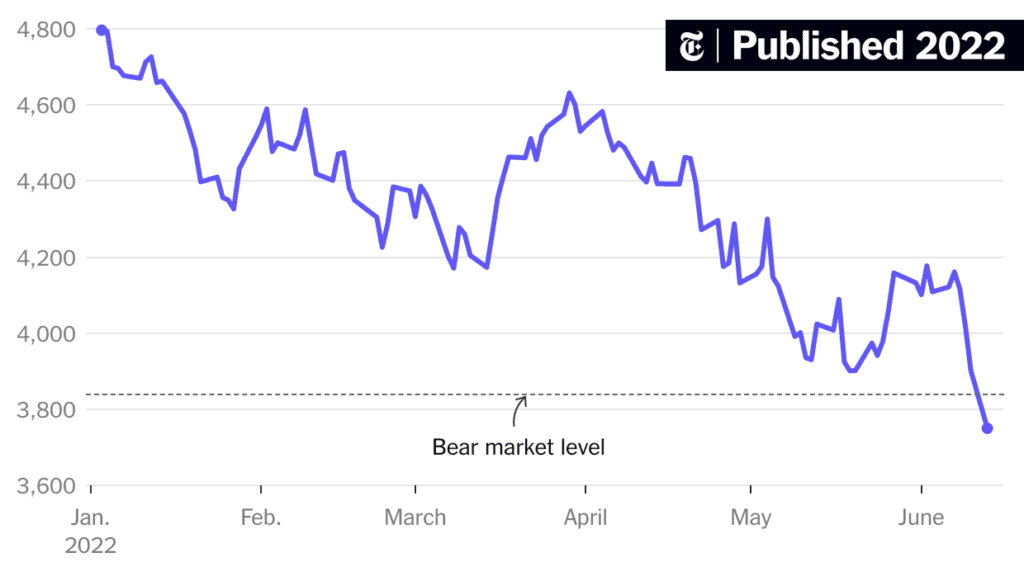
A financial crisis invariably engenders mispricings, enabling discerning investors to acquire high-quality assets at discounts. Optimal investment candidates include:
- Blue-Chip Equities – Companies with robust balance sheets, competitive moats, and consistent earnings resilience tend to outperform post-recovery.
- Dividend Aristocrats – Stocks with a history of stable and increasing dividends can generate income even amidst volatility.
- Broad Market ETFs – Exchange-traded funds tracking indices such as the S&P 500 provide diversified exposure to recovering markets.
- Contrarian Growth Investments – Identifying high-growth firms that are temporarily undervalued can yield asymmetric return potential.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
Long-Term Strategic Adjustments for Resilience
1. Portfolio Rebalancing Post-Crash
A market downturn frequently distorts asset allocation proportions. Systematic rebalancing—selling assets that have appreciated disproportionately and reinvesting in undervalued securities—ensures adherence to long-term investment objectives and mitigates portfolio drift.
2. Augmenting Financial Resilience
Beyond portfolio adjustments, strengthening one’s financial foundation is integral to withstanding economic shocks:
- Debt Optimization – Prioritizing the reduction of high-interest liabilities, such as credit card debt, safeguards financial flexibility.
- Emergency Fund Expansion – Augmenting liquid reserves to cover an extended duration of expenses fortifies resilience against prolonged downturns.
- Continuous Investment Discipline – Adhering to a systematic investment plan mitigates the adverse effects of market timing errors.
- Income Diversification – Establishing multiple revenue streams enhances financial security during periods of economic contraction.
3. Exploring Alternative Asset Classes
While equities remain the cornerstone of wealth accumulation, diversification across asset classes enhances stability. Considerations include:The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) – REITs provide real estate exposure with liquidity advantages over direct property ownership.
- Precious Metals – Gold and silver have historically functioned as hedges against inflation and economic distress.
- Cryptocurrency Allocations – Select cryptocurrencies exhibit low correlation with traditional assets, serving as potential hedges against fiat currency depreciation.
- Fixed-Income Securities – Government bonds, municipal bonds, and inflation-protected securities stabilize portfolios in high-volatility environments.
- Commodities and Inflation-Protected Assets – Energy, agriculture, and industrial metals serve as inflationary hedges in stagflationary periods.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
4. Deriving Empirical Insights from Market History
A retrospective analysis of past market crises provides invaluable lessons. Studying historical downturns—such as the Great Depression, Black Monday (1987), the Dot-Com Bubble (2000), and the Global Financial Crisis (2008)—illuminates recurring patterns and informs robust investment decision-making.
Maintaining an investment journal that documents strategic decisions, emotional reactions, and market observations fosters enhanced decision-making over successive cycles. By synthesizing empirical data with contemporary market intelligence, investors can refine their methodologies and cultivate superior resilience against future volatility.
Conclusion
Stock market crashes, while disconcerting, do not necessitate indiscriminate liquidation or hasty reactionary measures. Investors who approach downturns with analytical rigor, disciplined capital allocation, and a long-term perspective position themselves for superior wealth accumulation in subsequent recoveries. By integrating historical insights, quantitative risk management techniques, and behavioral finance principles, market participants can transcend short-term turbulence and achieve sustained financial prosperity.The Stock Market Is Crashing 5 years
Ultimately, enduring success in equity markets is predicated not on avoiding volatility but on leveraging it strategically to maximize long-term capital appreciation.